Allied Telesis – Network Access Control (NAC)
Advanced edge security for Enterprise networks
To effectively defend the network against internal threats, network administrators need secure LAN switches that provide protection against common attacks. They also need to implement policies that ensure that each device connecting to a network is as secure as possible. This combination of secure LAN switches and anti-malware policy can be very effective.
Allied Telesis switches have always provided a comprehensive range of defences to combat internal attacks. These attacks range from data stealing attacks, such as Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) spoofing, to Denial of Service (DoS) attacks such as Tear Drop or Ping of Death. Correct deployment of these defences can create a network that is impermeable to most of the harm these attacks cause.
NAC allows network administrators to automate policy enforcement. Rather than requesting that users ensure their devices conform to anti-malware policies, administrators can simply let the network do the job instead.
NAC has very quickly become an industry requirement, and is clearly much more than a new buzzword for network professionals. NAC offers an excellent way to control network access with automated policy enforcement, and to manage network security without vast administration overhead.
How NAC secures your network
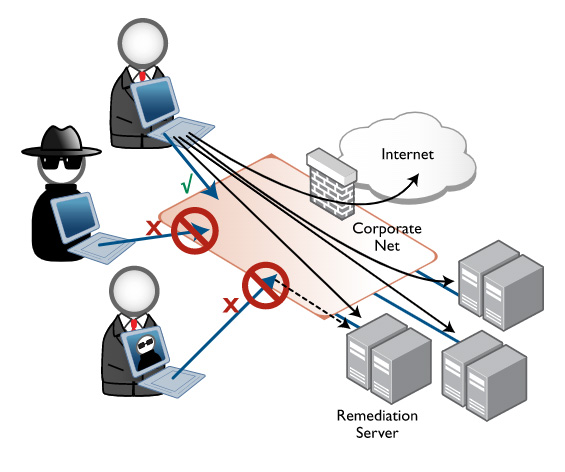
To provide this advance in network security, the significant elements included in Allied Telesis switch functionality are tri-authentication, roaming authentication, two-step authentication, and integration with NAC infrastructure.
1. Tri-authentication
Tri-authentication allows the network to identify all devices connecting to it. It can be used as part of a comprehensive NAC solution, or on its own where it provides a low overhead method of implementing network access security.
2. Roaming authentication
Mobile users move from one attachment point to another. Once a user has been given access, Allied Telesis roaming authentication ensures they are not inconvenienced by the need to re-authenticate as they roam.
3. Two-step authentication
Devices and users can be separately authenticated, to prevent sophisticated attempts to circumvent security.
4. Integration with NAC infrastructure
Allied Telesis equipment can integrate as a key component in network-wide NAC solutions.























