The Most Common Types Of Cyberattacks
Cyberattacks can be defined as an offensive and deliberate action of breaking into an organisations or individual’s network and devices. It is a breach of information, wherein the attacker undertakes such activities to seek benefits in terms of financial or other. Even with advanced technologies, companies still prey fall for cyberattacks. This may be because of a small carelessness from the employees or the security team. Employees who do not follow guidelines have become the top barrier to IT security. An alert of security patch ignored once can open the door for hackers to launch their attack.
How often do cyberattacks happens?
With the hit of covid 19 pandemic, the rise of cyberattacks have shown a tremendous hike because of remote working, it was the ideal time for hackers to get into company networks due to the vulnerabilities of remote working. FBI reported, 50% more attack attempts per week on corporate networks globally as of 2021. This percentage will again rise with the following years.
Now, let us discuss some of the most common types of cyberattacks.
1. Malware
Malware can be defined as a term which is used to describe malicious software which gets installed in your system without consent. This includes ransomware, spyware, viruses, trojans and worms. The attackers get into the network through vulnerabilities which generally includes clicking on an infected email attachment or links.
Among the malware attacks, ransomware seems to be the #1 types of cyberattack. Ransomware is a type of malware which enables the hackers to encrypt victim’s data. They demand for a ransom to be paid to provide the decryption keys, and threatens to publish or delete the data unless paid. 3 out of 4 organizations fell victim to a ransomware attack. Every hour of downtime due to a ransomware attack costs an average of $250,000.
Immediate actions you can take to protect against ransomware
- Update your software and security patches
- Raise awareness among employees about the risks involves in suspicious emails and attachments
- Backup your data offline.
- Secure and monitor you RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol)
2. Phishing
Phishing is one among the increasingly most common cyber threat. Phishing is a method of impersonating a company or an individual and sending fraudulent communications which appears to be genuine. But it contains malicious malware to hack into the victim’s system. The aim is to steal sensitive information from the users such as login and credit card details. Phishing emails can also include an infectious attachment to loads malware onto your computer and links that redirects you into downloading files.
3. MITM Attack
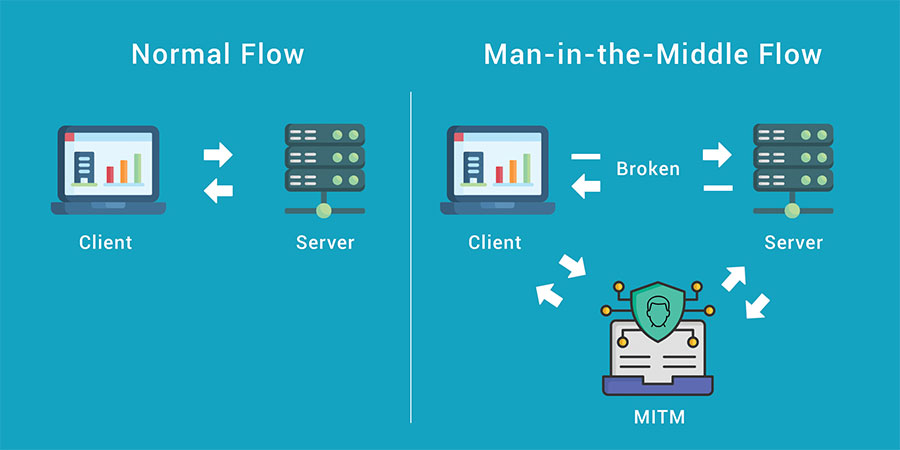
Man-in-the-Middle attack is type of cyberattack, wherein the attacker breaches into a network between two individuals or computers. The attacker can read and edit the data send back and forth, making the sensitive data vulnerable. It is called man-in-the-middle attack because the attacker places himself in the middle of a communication channel to manipulate data.
It is not easy to spot such attacks, as the data which is send from one end is revised or modified in mid-way and reaches to the receiver. It seems legit until something major occurs. The best way to stay vigilant ahead of such is to have a strong encryption on access points and use of VPN.
4. DoS and DDoS Attack
Denial-of-Service and Disrupted Denial-of-Service is another common type of cyberattack. The denial-of-service attack overwhelms a system’s resources making it unbale to respond to service request. DoS attacks are launched from a number of other hosts effected by the malware controlled by the attacker. DoS attacks doesn’t provide any direct benefits to attackers; however, DoS attacks can take a system offline to launch another cyberattack such as session hijacking etc.
5. Spoofing
Spoofing is kind of cyberattack where hackers impersonate themselves as a known or trusted source. The aim of the hacker is to get access into the target’s devices or network, steal sensitive information and for extorting money. It can also be for installing malware in the victim’s system. Cybercriminals trick the victims to provide their personal information and click on malicious links by acting to be a trusted source.
There are different kinds of spoofing, which includes; email spoofing, caller-ID spoofing, website or domain spoofing, IP spoofing, GPS spoofing, ARP spoofing etc.
6. Social Engineering
Social engineering is a type of cyberattack which relies highly on human interaction and involves manipulation of people into breaking security procedures. The hackers exploit human weakness to gain access to their personal and protected information. The four social engineering vectors are vishing, phishing, smishing and impersonation.
Here is an example of social engineering. Most websites have the option “forgot password” and reset them. If the password recovery system is not properly secured, hackers can easily gain access to your account.
7. Supply chain attack
Supply chain attack is another one of the most common types of cyberattacks that organisations encounter. The attackers target the weakest member of a supply chain network to tamper the distribution or manufacturing of a product by either installing hardware-based spying components or malware. Supply chain attacks are not limited to one industry. It can occur to any industry like information technology, industry resellers, government sector etc.
8. SQL Injections
SQL – Structured Query Language injection is one among the most common cyberattacks, where the hackers take advantage of websites which depends on databases to serve users. The attacker inserts a malicious code to the servers using SQL, and make the server reveal sensitive information. The SQL injection can be carried out by an attacker by simply inserting a malicious code in the search box of a vulnerable website. To protect your websites from SQL injection attacks, it is important to have least-privilege model and make sure that the code implemented against the database must be strong enough to prevent SQL injection attacks.
9. Zero-day Exploit
A zero-day (0-day) exploit is a kind of cyberattack where the attacker finds a vulnerability in a software and is not yet mitigated by interested parties. The hacker takes advantage of this situation to launch cyberattacks, and these types of attacks are most likely to succeed as there is no active defence. It is difficult to detect zero-day exploits since there is no patches or antivirus signatures to detect them.
But there are few ways to detect unknown software vulnerabilities of past, which includes;
- Vulnerability Scanning
- Patch Management
- Input Validation
10. Insider Threats
Organisations implement advanced cybersecurity solutions to prevent cyberattacks. But sometimes the most dangerous attacks occur from within the organisation. The insider attacker will be aware of the cybersecurity measures undertaken, thus take necessary steps to stay unnoticed and fly under the radar until they launch the attack. They can easily penetrate through the enterprise network, have access to a number of systems and even have privilege access for sensitive data.
One of the best ways to prevent and detect insider threats is to limit the employee’s access to sensitive data and always monitor employee activity. With artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies implemented in modern day comprehensive cybersecurity solutions, any change in the user or employee behaviour can be detected.